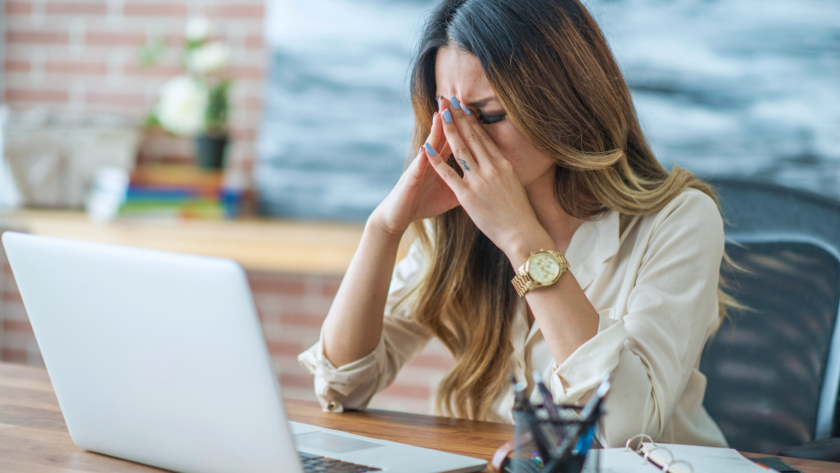
Stress is an unavoidable part of life, but its effects on mental health can be profound and far-reaching. Chronic stress significantly increases the risk of anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders. Increased levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, can alter brain function and lead to changes in mood and behavior.
Understanding the relationship between stress and mental health is crucial for effective management. Individuals experiencing high stress may find it difficult to cope with daily challenges, leading to a decline in overall well-being. Recognizing these patterns can empower people to seek help and implement strategies for stress reduction.
As the prevalence of stress continues to rise in modern society, its impact cannot be underestimated. By exploring the various ways stress affects mental health, individuals can better equip themselves to handle its challenges and foster a healthier state of mind.
Understanding Stress and Its Effects
Stress significantly influences both physical and mental health through various physiological mechanisms. The impact of stress hormones, particularly cortisol and adrenaline, activates the body’s stress response, which can lead to mental health challenges over time.
The Physiology of Stress
When an individual perceives a threat, the body initiates a stress response. This begins in the brain, where the hypothalamus activates the autonomic nervous system. The adrenal glands then release stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
Cortisol prepares the body for a fight-or-flight response by increasing energy availability, suppressing non-essential functions, and affecting mood and cognition. Adrenaline boosts heart rate and blood flow to vital organs. While this response is beneficial in short bursts, it becomes detrimental when activated persistently.
Stress Response and Mental Health
The stress response can lead to mental health issues, including anxiety and depression. Chronic activation of the stress response alters brain function, affecting neurotransmitter levels and neural connectivity.
High cortisol levels are linked to impaired memory, emotion regulation, and decision-making. These changes can cause increased feelings of distress, fatigue, and emotional instability. Prolonged stress may lead to clinical mental illnesses, affecting daily functioning and quality of life.
Chronic Stress and Its Long-Term Implications
Chronic stress results from prolonged exposure to stressors without adequate recovery. It can lead to significant health consequences, including cardiovascular disease, persistent anxiety, and depression.
The continuous release of cortisol impairs immune function and contributes to physical ailments. Individuals may experience fatigue, sleep disturbances, and a diminished ability to cope with stress. This cycle reinforces mental health problems, resulting in a challenging relationship between chronic stress and mental well-being.
Addressing chronic stress is vital for improving both physical and mental health, necessitating effective stress management techniques and interventions.
Consequences of Stress on Physical and Mental Wellness
Stress has significant implications for both physical and mental health. It can lead to various health problems, including cardiovascular issues and sleep disturbances, as well as an increased risk of mental disorders, such as PTSD and anxiety.
Stress and Heart Health
Chronic stress adversely affects heart health. When an individual experiences stress, the body releases hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones increase heart rate and elevate blood pressure.
Over time, this heightened state can lead to heart disease. Studies show a direct correlation between high blood pressure and elevated stress levels, contributing to the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Healthy coping mechanisms, such as regular exercise and mindfulness practices, can mitigate these effects, promoting better cardiovascular health.
Sleep Disturbances and Stress
Stress often disrupts sleep patterns, causing insomnia or poor sleep quality. Individuals under stress may find it challenging to fall asleep or stay asleep, largely due to racing thoughts and anxiety.
Lack of sleep can exacerbate stress, creating a vicious cycle that can lead to further health complications. Prolonged sleep deprivation can result in fatigue, reduced cognitive function, and weakened immune response.
Creating a calming bedtime routine may help restore a healthier sleep cycle, leading to improved overall wellness.
The Link Between Stress and Mental Disorders
High levels of stress are closely associated with various mental health conditions. Conditions such as anxiety disorders, depression, and PTSD can arise from prolonged exposure to stress.
Individuals experiencing traumatic stress may see an increase in symptoms related to these conditions. The chronic nature of stress can amplify feelings of fear, helplessness, and overwhelming anxiety.
Seeking professional help and implementing stress management strategies can play a crucial role in addressing these mental health challenges.
Strategies for Stress Management and Prevention
Effective management of stress is crucial for maintaining mental health. Various techniques and practices can reduce stress levels and enhance resilience. This section explores key strategies for relaxation, exercise, and the importance of building a support system.
Effective Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques are essential for managing stress. Methods such as meditation, mindfulness, and deep breathing exercises promote a calm mind.
- Meditation: This practice focuses attention and eliminates distractions. It involves sitting quietly and paying attention to thoughts, feelings, and the present moment.
- Deep Breathing: This simple technique helps lower the heart rate and relieve tension. Inhale deeply through the nose, hold for a moment, and then exhale slowly through the mouth.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This involves tensing and then relaxing each muscle group. It reduces physical stress symptoms effectively.
Incorporating these relaxation techniques into daily life can enhance mental clarity and reduce anxiety.
The Role of Exercise in Stress Reduction
Regular exercise is a powerful tool for stress management. Physical activity triggers the release of endorphins, which are natural mood lifters.
- Aerobic Exercises: Activities like running, swimming, or cycling can significantly reduce stress. They increase heart rate and stimulate circulation.
- Yoga: Combines physical postures, breathing techniques, and mindfulness. It promotes overall well-being and can effectively relieve stress.
- Consistency: Engaging in exercise regularly leads to better mental health outcomes. It builds resilience against daily stressors.
Incorporating exercise into a routine supports both physical fitness and mental health.
Building a Support System for Better Mental Health
A strong support system plays a critical role in managing stress. Connection with others can foster a sense of belonging and security.
- Friends and Family: Sharing thoughts and feelings with loved ones can alleviate stress. Providing and receiving empathy strengthens relationships.
- Support Groups: Joining community groups or online forums allows individuals to share experiences. Connecting with those facing similar challenges can provide valuable coping strategies.
- Professional Help: Therapists and counselors offer expert guidance. They provide coping mechanisms tailored to individual needs.
Building and maintaining a solid support system enhances resilience and facilitates better mental health management.